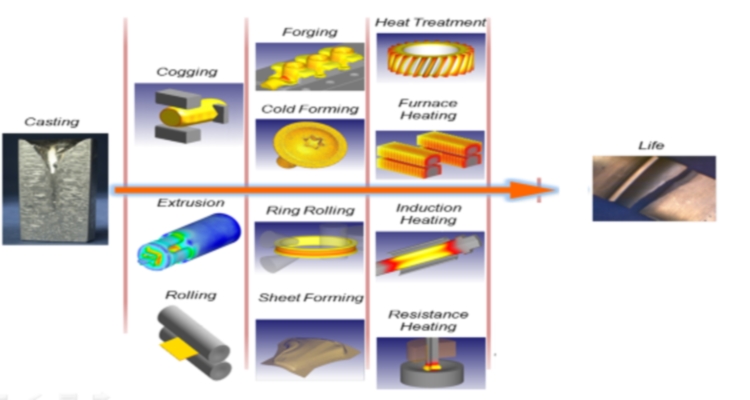
Metal Forming
Metal Forming, is a metalworking process of making metal parts and various objects by means of mechanical deformation. In this process, the workpiece is reshaped without any addition or reduction of material; keeping the mass unchanged. This process works on the phenomenon of plastic deformation, wherein the physical shape of the object is changed forever. In order to achieve this change, force greater than the yield strength of workpiece is applied.
Once the stress level on material surpasses its elastic deformation level, it undergoes plastic deformation. In plastic deformation, the geometric change undergone by material isn’t directly proportional to stress, hence causing permanent geometric change even after the stress is released.
Metal forming has much uniform characteristics throughout its processes, when compared to other contemporary processes like cutting & joining.
On the industrial scale, forming is characterized by:
- Higher requirement of loads & stresses ranging between 50 & 2500 N/ mm2
- Heavy, huge and expensive machinery is needed to accommodate the desired higher stresses and loads.
- Production is achieved with many parts, to capitalize on the economy of production and pay off for the expenditure of the machine tools.
Different Types Of Metal Forming Processes
Metal forming processes can be classified into two major groups on basis of surface area to volume ratio; bulk deformation and sheet metal working processes. Bulk deformation is characteristic in that the work formed has a low surface area to volume ratio. In sheet metal working, the metal being processed will have a high surface area to volume ratio. The following is a brief overview of the major metal forming processes of both types of metal forming.
Bulk Deformation:
Rolling: In rolling processes, rolls are used to cause deformation of the workpiece. This processes includes flat rolling, thread rolling, shape rolling along with production of seamless pipes and tubes with rotary tube piercing.
Forging: In forging dies are used to compress and shape the workpiece. These dies can be flat or somtimes have geometry of the desired shape.
Extrusion: Extrusion involves forcing the metal through die opening, thereby producing work of variable length and constant cross-section.
Drawing: The major difference between drawing and extrusion is that here the length of metal is passes through die opening thereby causing forming on its cross section. The difference between drawing and extrusion is the application of force to the work piece. In extrusion the work is pushed through the die opening, in drawing the work is pulled through the die opening.
Sheet Metal Working
Bending: Bending involves the deformation of the work by way of bending about a certain axis.
Deep Drawing: Deep drawing is a metal forming process in which a flat piece of plate or sheet is forced into a die cavity to take a shape, such as a cup.
This entry was posted on Tuesday, May 5th, 2015 at 5:29 pm and is belong to category Blog.




